Understanding Artificial Intelligence: History, Types, and Applications
What is AI?
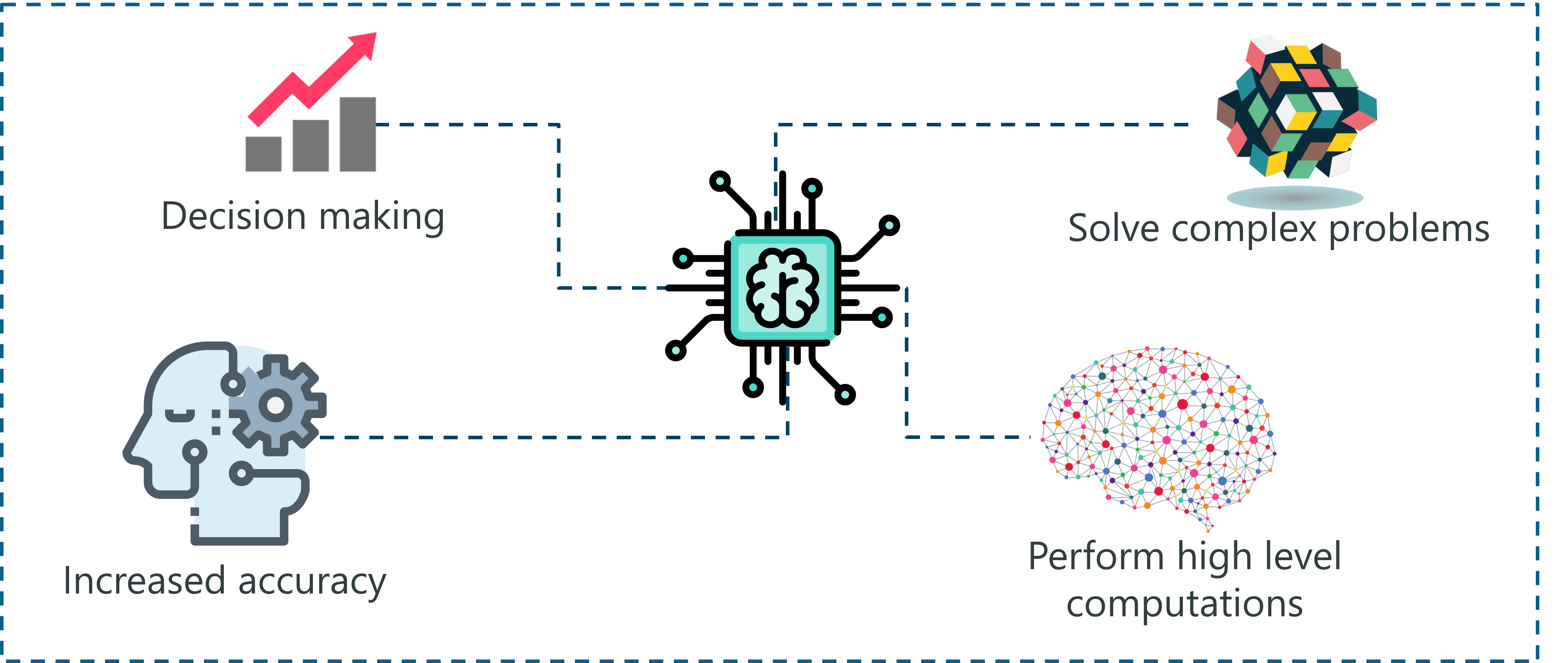
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think, learn, and make decisions similar to how humans do. AI systems can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as understanding natural language, recognizing patterns, and solving complex problems.
Key Points:
Definition: AI involves creating algorithms and models that enable machines to perform tasks that would normally require human intelligence.
Goal: The primary goal of AI is to create systems that can operate autonomously, adapt to new situations, and improve their performance over time.
History of AI
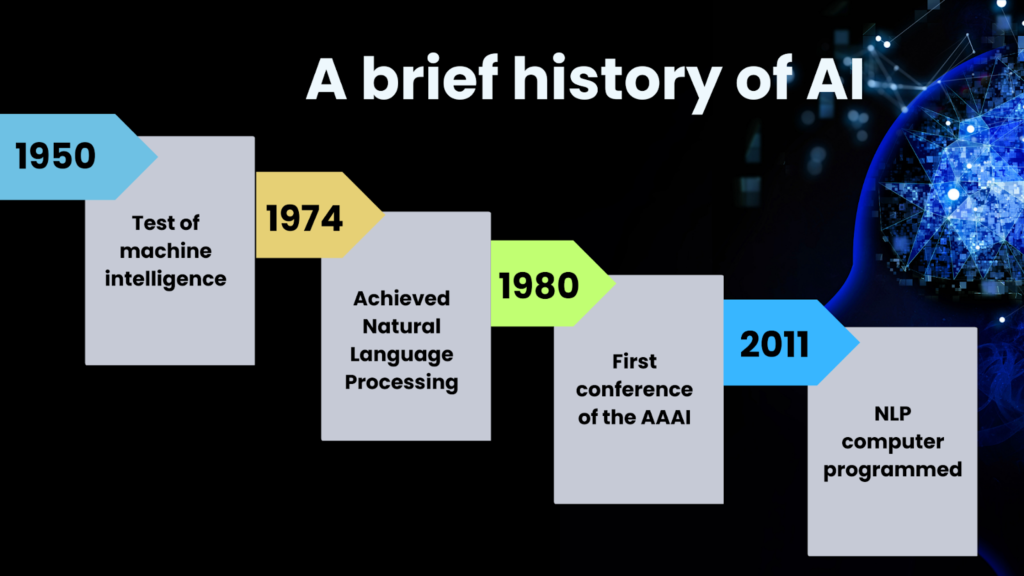
AI has a rich history that dates back to the 1950s. Here’s a brief overview:
The 1950s-1960s: The concept of AI was first introduced by Alan Turing, who proposed the idea of a "universal machine" capable of simulating any other machine’s behaviour. The term "Artificial Intelligence" was coined by John McCarthy in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference.
1970s-1980s: The field saw significant progress with the development of early AI systems and expert systems designed for specific tasks, such as medical diagnosis.
1990s-2000s: AI research gained momentum with advances in machine learning and computational power. Notable achievements include IBM's Deep Blue defeating chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997.
2010s-Present: AI has become more mainstream with breakthroughs in deep learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. Examples include Google's AlphaGo defeating the world champion Go player and the widespread use of virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa.
Types of AI
AI can be categorized into different types based on its capabilities and functionalities:
- Narrow AI (Weak AI):
- Definition: AI systems designed to perform specific tasks or solve particular problems.
- Examples: Voice assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa), recommendation systems (e.g., Netflix, Amazon), and image recognition software.
- Definition: AI with generalized human cognitive abilities, capable of understanding, learning, and applying knowledge across a wide range of tasks.
- Current Status: General AI is still theoretical and has not yet been achieved.
- Definition: Hypothetical AI that surpasses human intelligence in all aspects, including creativity, problem-solving, and emotional understanding.
- Current Status: This is a future concept and remains speculative.
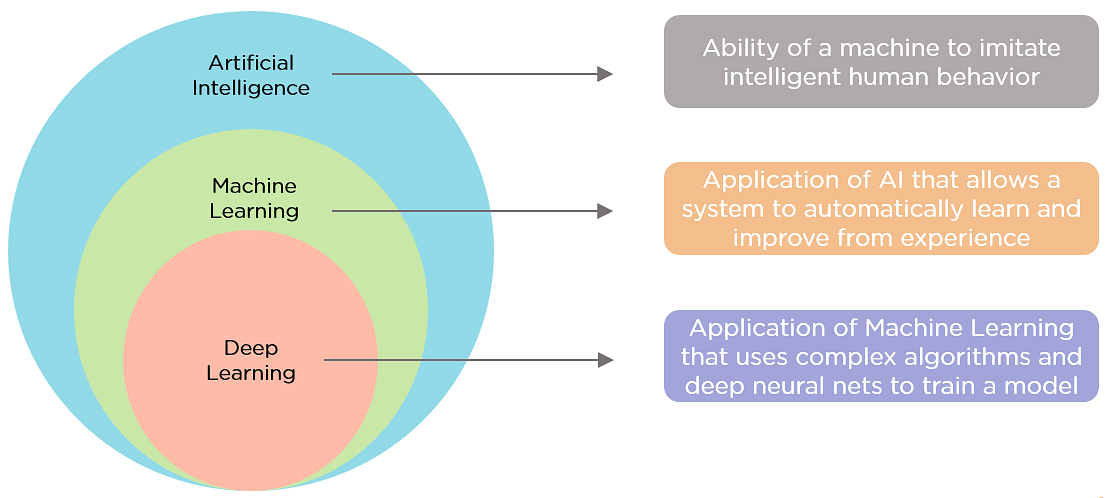
AI vs. Machine Learning vs. Deep Learning
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The overarching field that encompasses all technologies and methods for creating intelligent systems.
- Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI that involves training algorithms to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. Examples include regression analysis and clustering.
- Deep Learning (DL): A subset of ML that uses neural networks with many layers (hence "deep") to model complex patterns in data. Examples include image and speech recognition.
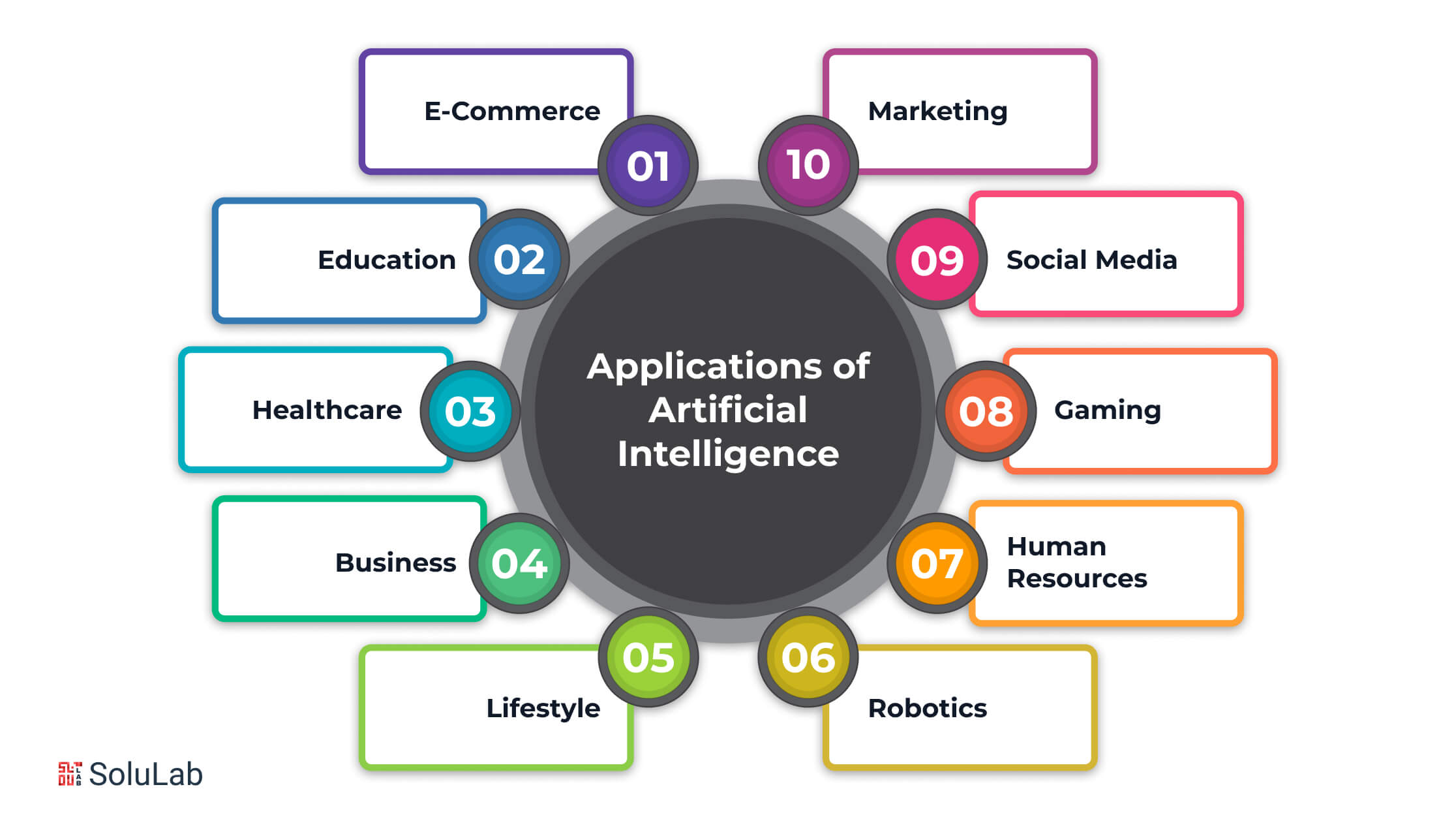
Applications of AI
- Healthcare: AI is used for diagnosing diseases, personalizing treatment plans, and predicting patient outcomes.
- Finance: AI helps with fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and risk management.
- Retail: AI enhances customer experiences through personalized recommendations, inventory management, and chatbots.
- Transportation: AI powers autonomous vehicles, traffic management systems, and route optimization.


Comments
Post a Comment